 |
Intro | Anatomy of a Class | Constructors | Accessor Methods | Mutator Methods | Static Variables | Game |
Anatomy of a Class
This notebook will explain the structure of a class in Java, including attributes, methods, and instantiation. It will also include examples and a mini-project that requires fixing broken code.
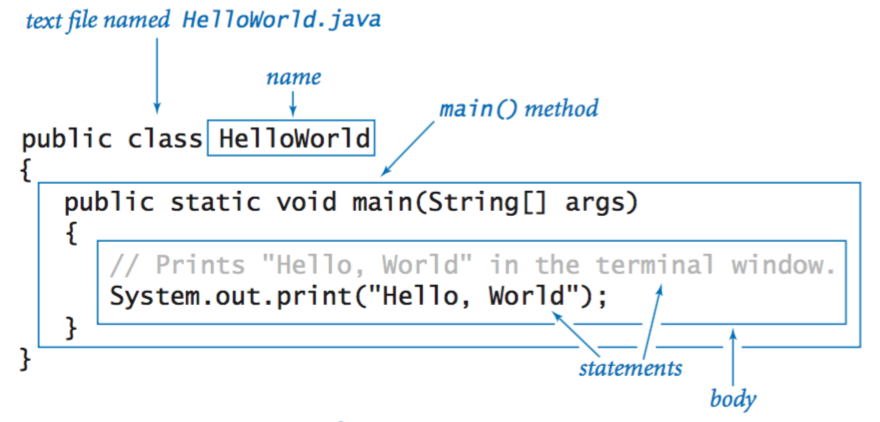
1. Introduction to Classes
- A class in Java is a blueprint for creating objects. It defines a data structure that includes methods and attributes.
- Example:
public class Car {
// Attributes
String model;
int year;
// Method
void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving the car.");
}
}
This Car class has attributes model and year, and a method drive() that prints a message.
2. Attributes and Methods
- Attributes (or fields) are variables that belong to an object.
- Methods are functions that belong to a class.
- Example:
public class Person {
// Attributes
String name;
int age;
// Method
void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
In this Person class, name and age are attributes, and greet() is a method.
3. Constructor
- Constructors are special methods used to initialize objects.
- They have the same name as the class and do not have a return type.
- Example:
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
// Constructor
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
This Person class includes a constructor to initialize name and age.
4. Class vs. Instance Variables
- Instance variables are attributes specific to each object.
- Class variables (static variables) are shared among all instances of the class.
- Example:
public class Car {
// Class variable
static int numberOfCars = 0;
// Instance variables
String model;
int year;
// Constructor
public Car(String model, int year) {
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
numberOfCars++;
}
}
Here, numberOfCars is a class variable that keeps track of how many Car objects have been created.
5. Mini Project: Fix the Code
- Below is a class with broken code. The goal is to fix the class so it properly initializes and uses instance variables.
-
Broken code:
- Task: Debug the
Bookclass so it correctly initializestitleandauthor. Consider how the constructor should be modified.
public class Book {
String title;
String author;
// Broken constructor
public Book(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
}
- Task: Debug the
Bookclass so it correctly initializestitleandauthor. Consider how the constructor should be modified.
Comments
You are seeing this because your Disqus shortname is not properly set. To configure Disqus, you should edit your
_config.ymlto include either adisqus.shortnamevariable.If you do not wish to use Disqus, override the
comments.htmlpartial for this theme.